The AI race is heating up. Tech companies are betting on GenAI, rolling out flurries of new tooling and technologies. Experts predict that the market around it will continue to expand in 2024 and beyond.
But AI’s booming growth raises questions about how smaller companies are going to sustainably tap into this red-hot market without pouring more money than they have.
Cost of infrastructure and technical expertise are the two chokeholds of bootstrapped and smaller organizations, according to polls. “We know a lot about AI from where we stand today, but in reality, we don’t, not unlike Edison and Westinghouse in the early days of electricity. Like them, we don’t fully understand the opportunity that’s in front of us,” says Brandon Royal, Product Manager for AI Infrastructure at Google Cloud, during a presentation at the recent AI Field Day event.
For enterprises that are feeling their way through, Google Cloud has come forward selling them compute power that they require to build AI solutions in-house, off of its robust infrastructure.
When it comes to AI, Google is talking big game. With one eye set on the Gen AI play, Google has its other eye fixed on AI infrastructure. For what it’s worth, Google Cloud owns one of the biggest digital infrastructures in the industry that it has perfected for years, cramming in new features, and expanding the scope and scale. Customers are confident about the platform’s capabilities and offerings. Now in the age of AI, it is the superhighway of innovation.
The Rise of Open AI Models
In the timeline of artificial intelligence, open models mark a significant turning point. The massive innovation going on in open models points to their true potential.
Open models are an important part of GenAI strategy, says Royal. These models are budget-friendly, adaptive to finetuning, and can be optimized for a range of very specific tasks. Cherry on top, they can be deployed flexibly on a variety of platforms.
“A lot of 2023 was about building the foundation models and getting up to a point where all these AI models were usable. A focus area of 2024 will be adopting those models. Fine tuning and inference will start to take over as we go into the next year,” he predicts.
Google has joined the effort of creating and spreading GenAI to the users like its industry peers. The new Gemini is Google’s state-of the-art multimodal model.
“Gemini is the most flexible model that we have, and the most powerful one that we deliver to our customers. It is built essentially on the same AI infrastructure that we provide customers,” Royal says.
Being multimodal, it can respond to not just text prompts, but voice, video, audio and code. Like conversational chatbots, it can, first and foremost, answer questions in natural language. But unlike many, it can also take actions like placing a phone call, making a booking, setting an alarm, and so on.
One of its superpowers is to analyze images with remarkable precision. Gemini can also help programmers write code. Google says it can role-play in a number of other scenarios as well.
Gemini comes in multiple flavors and is integrated throughout the Google product suite from Workspace to Android OS to Google Cloud.
Recently, Google opened access to the technology with the release of AI model, Gemma. Gemma is a family is lightweight open models – 2B and 7B parameters precisely – and are built from the same research and technology as Gemini. It is developed by Google DeepMind, and is available as an online service for users, informs Royal.
In the past, free sharing of proprietary technologies was viewed as a losing strategy, leading organizations to be secretive about their innovations for years. But that thought is fast losing ground as companies like Google are putting their technologies out and sharing them with independent developers, external companies, and the community at large.
A Fully Outfitted AI Infrastructure
But where Google Cloud truly shines is in the AI infrastructure space. “70% of the most impactful GenAI unicorns choose Google Cloud for AI infrastructure and platforms,” says Royal. These include front-line companies like Anthropic, Cohere and Character.ai, that are engaged in model development.
Google Cloud offers the beefiest AI platform and infrastructure to deploy large language models. It constitutes massive clusters spanning thousands of processors and nodes. On Google Cloud, users can scale up to 50K TPU chips and 15K nodes per cluster, the highest in the industry – particularly useful when doing large-scale training.
But slimmer configurations are not excluded from its scope of offering. Google Cloud puts forward a most exhaustive selection of hardware options – TPUs, GPUs, CPUs – to support all classes of AI workloads in training, finetuning and inference categories.
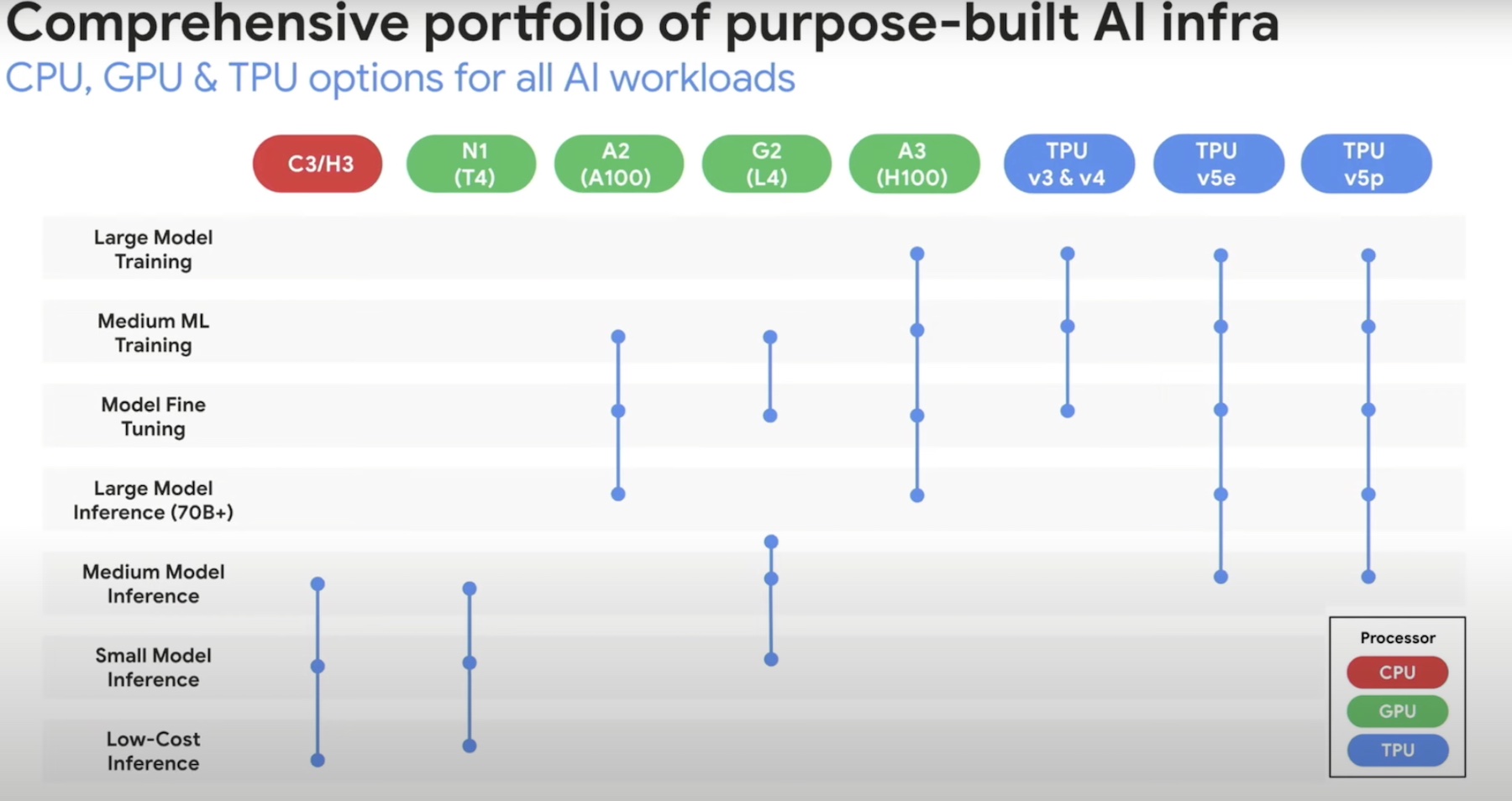
It has the largest selection of accelerators in the market. “We often talk about big bad hardware, like TPUs and GPUs, and specialized accelerators for running AI workloads, but I think it’s an important reminder that a lot of these journeys still exist on CPUs,” Royal points out.
In inferencing where the models are light and nimble, CPUs make the primary architecture. Intel Xeon Scalable Processors are battle-tested for these specific workloads. Royal highlights AMX or Advanced Matrix Extensions, the embedded AI block in Xeon CPUs, as an exemplary technology for non-classic AI workloads. Powering both Sapphire Rapids and Emerald Rapids, AMX provides an easy way to keep up with the demands of AI workloads without pumping money in specialized hardware.
Royal cites the story of Palo Alto Networks, a customer that used Intel Sapphire Rapids with Intel AMX instruction set for low-latency inference in deep learning models, and experienced twice the performance of Ice Lake that was pre-AMX, for some inline models.
At the high-end of Google Cloud’s offering is Cloud Tensor Processing Units or TPUs. These are Google’s custom silicon purpose-built for machine learning use cases. Royal emphasizes that the TPUs are a rapidly iterating product and is custom-made for every customer.
GKE for Managed K8s Orchestration
Container technology has bubbled up as critical for training and inferencing of massive-scale models. Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) incorporates Kubernetes’ efficiency and flexibility of orchestration into Google Cloud. GKE is a fully managed Kubernetes service available on Google Cloud Platform.
It has two modes of operation – Standard, where Google Cloud manages the control plane but customers handle the configuration settings, and Autopilot for a fully-managed service. Autopilot is the default mode of operation when a cluster is deployed in GKE. It performs sundry orchestration tasks – provisioning, auto-scaling, and lifecycle management, giving users the best hands-off Kubernetes experience.
Royal highlighted Google Cloud’s pod-level SLA which is a step-up from the usual node-level SLA that most providers offer. “We take a higher degree of responsibility for customers that are deploying their AI models in GKE,” he says.
For more, check out Google Cloud’s presentations with Intel, from the AI Field Day event. Also give Alastair Cooke’s article on this a read on the Futurum Group’s website.