The IT industry has gone through heavy loops of change in the recent years, reflected in the changing market trends and customer expectations. These changes include skyrocketing growth of HPC workloads, and demand for blazing-fast storage systems that can deliver faster and faster loading times.
Vendors have rose to the occasion bringing to the market newer SSDs that outperform the previous generations by miles. But many of them end up providing more power than is actually required to run these workloads, resulting in unused resources and cost overruns.
The onset of a demand for right-sizing SSDs is cascading through users shuffling between powering high-performance workloads and trimming down costs.
The New D7-P5810
Solidigm just dropped a new SLC SSD, the D7-P5810, which they unveiled at the recent Storage Field Day event, that will likely lead the storage market for these workloads. Combining ultra-high endurance with supreme cost efficiency, the new product strikes a perfect balance, and is going to play a key role in accelerating write-intensive workloads.
The product is an addition to Solidigm’s flagship D7 family of SSDs, one of their highest preforming ranges. Although superior speed and performance span all of the previous generations of products in the D7 lineup, the P5810 is streets ahead of all the older models.
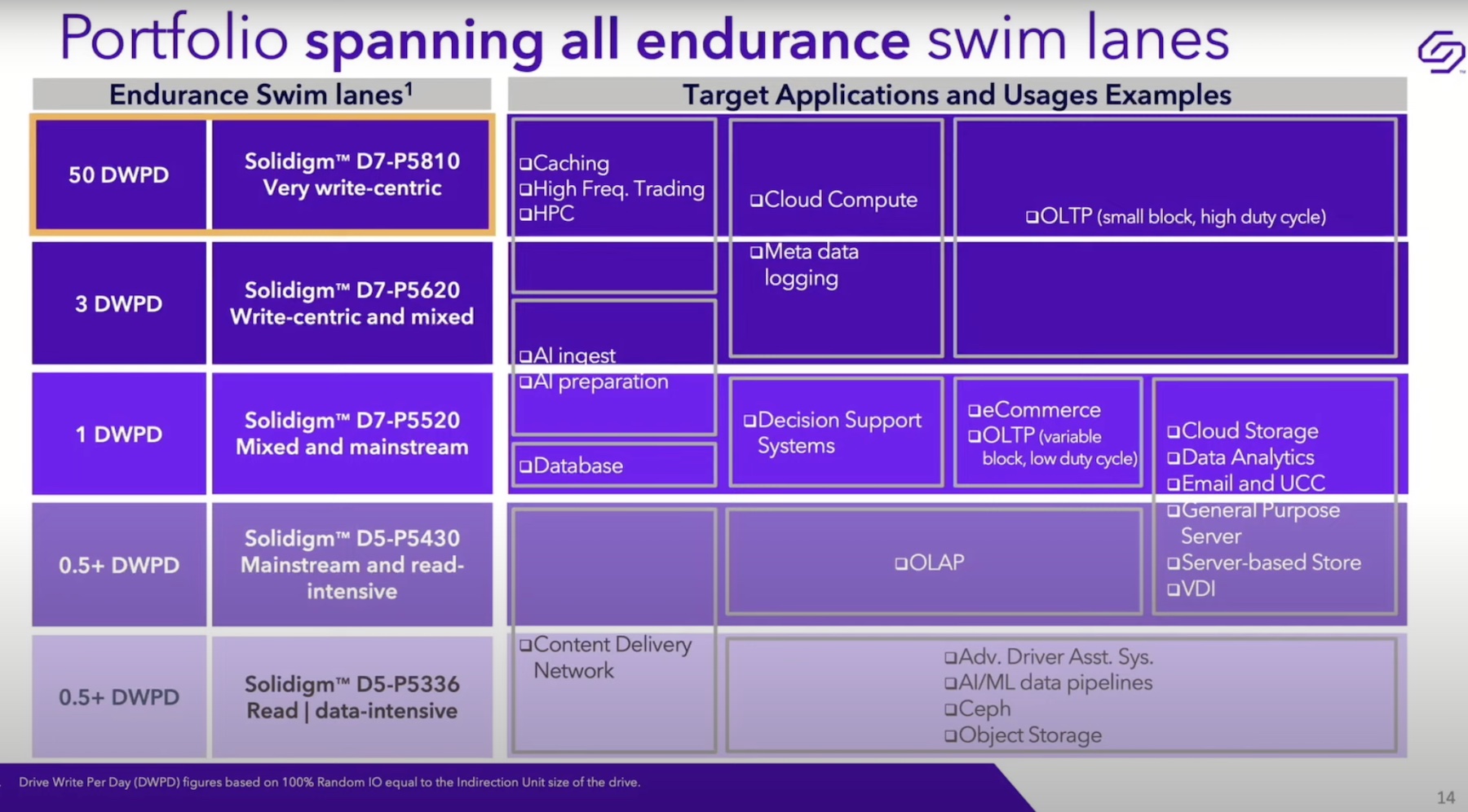
D7-P5810 crowns the Solidigm endurance swim lane chart, offering a whopping 50 Drive Writes Per Day (DWPD) for random writes, and 65 DWPD for sequential writes, compared to the medium 1DWPD and 3DWPD endurance of its older siblings.
The D7-P5810 is a 144L 3D NAND drive that uses a trie and true media technology. “It is built on a NAND media that we introduced back in 2021 with our TLC product line, and we have SSDs on 144 layer which is QLC and TLC since the past two years now,” said Ratnesh Muchhal, Data Center Product Marketing Engineer, during the presentation.
As noted, the D7-P5810 is a single-level cell (SLC) NAND SSD, that stores one bit of information per cell as opposed to QLC’s 4 bit per cell, leading to much faster writes and retrievals. Both NAND and SLC technologies inherently offer a host of advantages such as low cost per bit, power-loss protection, high endurance and top-tier performance. The Solidigm D7-P5810 tops that with best-of-breed write-centric features.
Targeted at the most demanding write-intensive and high-endurance workloads like write cache, HPC, high-frequency trading, logging, journaling, OLTP, and sundry, that put high write pressure on the drives, the product perfectly complements Solidigm’s line of read-intensive QLC drives.
D7-P5810 outpaces the performances of several products in its league, specifically Kioxia and Micron where random write IOPS are concerned.
“The drive is built for two specific purposes – a) the high writes per day is intended for write caching, heavy logging kind of algorithm and applications and, b) in terms of the write performance, we are able to deliver 2x performance of our nearest competition,” Muchhal said.
However, with sequential write IOPS, that number dips slightly, but is still at par with the competitors.
A Significant Cost Relief
Compared to the other storage-class memory (SCM) alternatives in the market, the D7-P5810 operates with much less power. It has active and idle power draws of 12W and 5W. Even working at top speed, it achieves the high perf numbers within the 12 Watt power envelope.
Solidigm says that D7-P5810 undercuts competitor non-NAND technologies by a wide margin, offering SCM performance at only 20% the cost.
“We are able to offer the high endurance, and higher write capabilities at about 20% of the cost of existing technologies out there,” said Muchhal.
The D7-P5810 comes in a U.2 (15mm) form factor, and is currently available in 800GB capacity. For now, Solidigm is focusing on manufacturing the 800GB model in high volume, but announced that a bigger 1.6TB model is underway and will likely hit the market early 2024.
To optimize the performance further, Solidigm has designed an open-source Flash Translation Layer (FLT) software called Cloud Storage Acceleration Layer (CSAL). The CSAL is powered by advanced algorithms that unlock smarter allocation of resources, minimum latency and overall faster access to data.
CSAL sits between the SSDs and applications, facilitating write requests and amplifying write performance, essentially extending the value of its SSDs to more workloads. Using D7-P5810 and it’s QLC SSDs as cache and write buffer, it write-shapes workloads to NAND- compatible sequential writes. All hot data gets written in the SLC drives, which when turns cold, is shifted to the high-capacity QLC drives for cost optimization.
Be sure to watch Solidigm’s deep-dive presentations of D7-P5810 and CSAL from the recent Storage Field Day event for more technical details.