Although we use Intel’s NUC as a shorthand for the type of hardware deployed at the far edge, this recently-cancelled platform isn’t all there is. This episode of Utilizing Edge looks beyond the NUC, to platforms from Lenovo, Nvidia, and more, with Julian Chesterfield of Sunlight, Andrew Green, and Stephen Foskett. ARM-based solutions, many using the Nvidia Jetson platform, are particularly interesting given their low cost and power consumption and strong GPUs for edge AI. A hyperconverged stack runs all of the components required for high availability, including storage and networking, in software spanning all of the nodes in a cluster, and this is commonly deployed on low-cost devices at the far edge. The trend to deploying applications at the edge is driven both by new hardware and software capabilities and the changing expectation of consumers and businesses.
In breaking news, Intel, a prominent player in the edge computing hardware market, has announced the discontinuation of its investment in the Intel NUC (Next Unit of Computing). The Intel NUC, a popular choice for edge deployments due to its compact form factor, has sparked speculation within the industry about what alternative devices will fill this void.
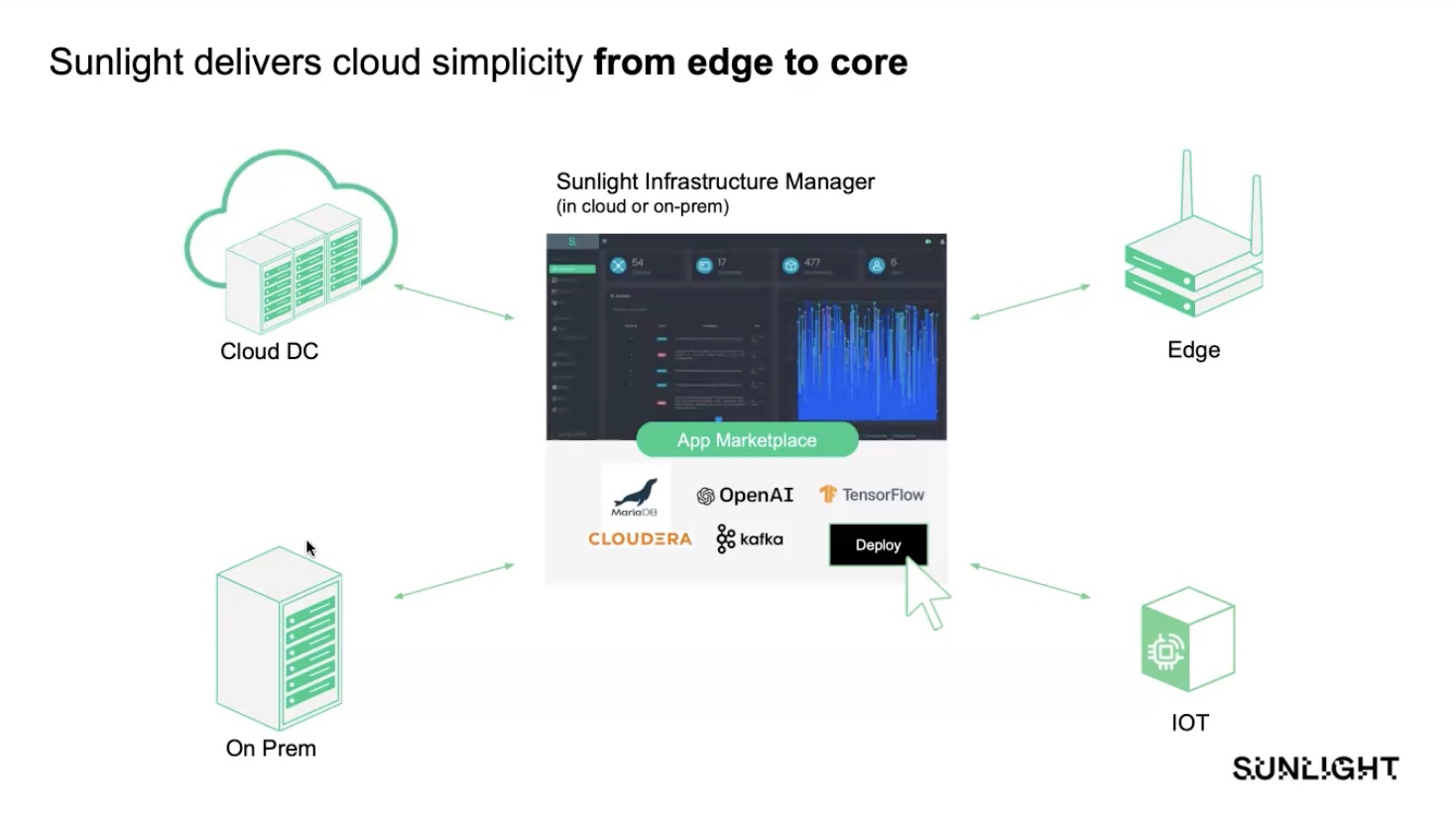
To shed light on the diverse world of edge devices, Sunlight, a leading company well-versed in various PC platforms and low-powered alternatives, joins the Utilizing Tech podcast. Julian Chesterfield from Sunlight emphasizes that the industry’s focus on Intel NUCs does not fully reflect the wide range of devices used at the far edge. Sunlight offers a full virtualization platform that runs on small, lightweight hardware platforms, as well as larger data center infrastructure, providing scalability and flexibility for edge deployments.
Among the purpose-designed devices for edge computing, the NVIDIA Jetson platform stands out for its capabilities in computer vision processing and AI workloads. It offers a tailored solution for these demanding edge applications. Additionally, Lenovo, a key player in the small form factor computer market, presents its Think Edge portfolio, which includes devices based on both Intel and ARM processors. Lenovo’s offerings cater to various edge computing requirements and provide options for different use cases.
While Intel has been a dominant force in the edge computing hardware space, the ARM architecture is gaining traction, particularly for power-efficient servers and lightweight platforms. ARM-based solutions offer cost-effectiveness and energy efficiency, making them ideal for widespread deployment across numerous distributed edge sites.
The conversation about edge computing extends beyond hardware and architecture. Security is a critical concern in edge deployments, encompassing physical security and runtime security. Sunlight emphasizes the importance of trusted boot and maintaining control over access to services and the integrity of data from IoT devices. To address these challenges, Sunlight has partnered with Edgelabs to provide a distributed edge security perimeter solution. This collaboration enhances security measures, including intrusion detection and prevention systems, and allows for centralized management and control of edge environments.
As edge computing gains momentum, organizations are seeking control over the types of devices deployed at the edge. The ability to scale resources to accommodate lightweight IoT sensors as well as high-computational devices is a significant challenge. Sunlight’s hyper-converged edge stack offers a solution by providing redundancy and resiliency across multiple physical nodes, creating highly available systems in software rather than relying solely on expensive redundant hardware.
Various industries are showing significant demand for edge deployments. The hospitality sector, including retail and quick-service restaurants, aims to optimize costs while enhancing service quality through smart technology adoption. Supermarkets leverage edge technology to monitor refrigeration units and ensure optimal performance. In the energy sector, both traditional oil and gas environments and renewable energy sectors benefit from edge computing, enabling autonomous decisions, efficient production processes, and monitoring of solar panels and wind farms. The industrial sector leverages edge computing for factory automation, quality control, and safety monitoring, enabling smarter operations and enhanced efficiency.
The edge represents a paradigm shift from traditional on-premises deployments, requiring hyper-converged, low-power, and low-demand solutions. Edge deployments bridge the gap between IT and the real world, bringing technology into physical environments and addressing challenges such as extreme temperatures, rugged conditions, and remote locations. The flexibility, scalability, and simplicity of edge solutions are key factors driving their adoption.
Hosts and Guest:
- Stephen Foskett, Publisher of Gestalt IT and Organizer of Tech Field Day. Find Stephen’s writing at GestaltIT.com and on Twitter at @SFoskett.
- Andrew Green, research analyst at GigaOm. Check out his work on the GigaOm website and connect with him on LinkedIn.
- Julian Chesterfield, CTO and Founder of Sunlight.io. You can connect with Julian on LinkedIn and find out more about Sunlight.io on their website and their newsletter.
For your weekly dose of Utilizing Edge, subscribe to our podcast on your favorite podcast app through Anchor FM and check out more Utilizing Tech podcast episodes on the dedicated website, https://utilizingtech.com/.