Edge environments are rapidly gaining importance as companies shift their services to network edge locations. Advanced solid-state drives (SSDs) play a crucial role in these environments, offering high performance, reliability, energy efficiency, and storage density. Server vendors are adopting the EDSFF SSD form factor to meet the demands of edge computing, improving the electrical, mechanical, and logical capabilities of SSDs. Solidigm has demonstrated the reliability of QLC flash over four generations, and their D5-P5430 SSD in the new E3 form factor maximizes efficiency and capacity at the edge. With faster speeds, higher endurance, lower power consumption, and compact size, advanced SSDs are essential for unleashing the full potential of edge computing.
The Emergence of the “Near Edge”
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the concept of edge computing has gained significant traction. While we often delve into the realm of the “far edge” on Utilizing Tech, it is essential not to overlook the emerging importance of the “near edge.” As companies increasingly move their services from traditional datacenters and cloud environments, they are setting up shop in network edge locations, including 5G points of presence. The success of these operations heavily relies on the deployment of flexible, reliable, energy-efficient, and dense edge servers. One crucial component that plays a significant role in achieving optimal performance in these servers is the advanced solid-state drive (SSD).
The near edge refers to the network edge locations that are becoming the new hubs for delivering services and processing data. These locations, strategically positioned closer to end-users, enable lower latency, reduced bandwidth requirements, and improved overall performance. As the demand for real-time applications and ultra-responsive services grows, companies are shifting their infrastructure to the near edge. This paradigm shift has created an increasing need for edge servers that can meet the demands of this dynamic environment.
The Role of Advanced SSDs in Edge Environments
Storage is a critical component in edge servers, as it directly impacts the overall performance and responsiveness of applications. Traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) fall short when it comes to meeting the requirements of edge environments due to their slower read and write speeds and mechanical aspects, including power and cooling requirements and reliability issues in adverse conditions. In response, server vendors are turning to advanced SSDs and are increasingly adopting the Enterprise and Data Center Standard Form Factor (EDSFF), for their edge server solutions. But EDSFF has moved beyond the old “ruler” SSD to include short and long devices better suited for compact edge servers.
The advantages of advanced SSDs in edge environments are manifold. These cutting-edge storage solutions offer faster read and write speeds, significantly reducing data access latency. They also provide high endurance, ensuring consistent performance over extended periods of heavy workloads. Modern SSDs also consume less power, making them more energy-efficient and requiring less cooling in edge deployments where environmental are a critical factor. Furthermore, the compact form factor of SSDs allows for higher density in edge servers, enabling organizations to maximize their computing resources within limited physical spaces. And these modern devices are more rugged and reliable in harsh environments.
Reliability of QLC Flash in Edge Servers
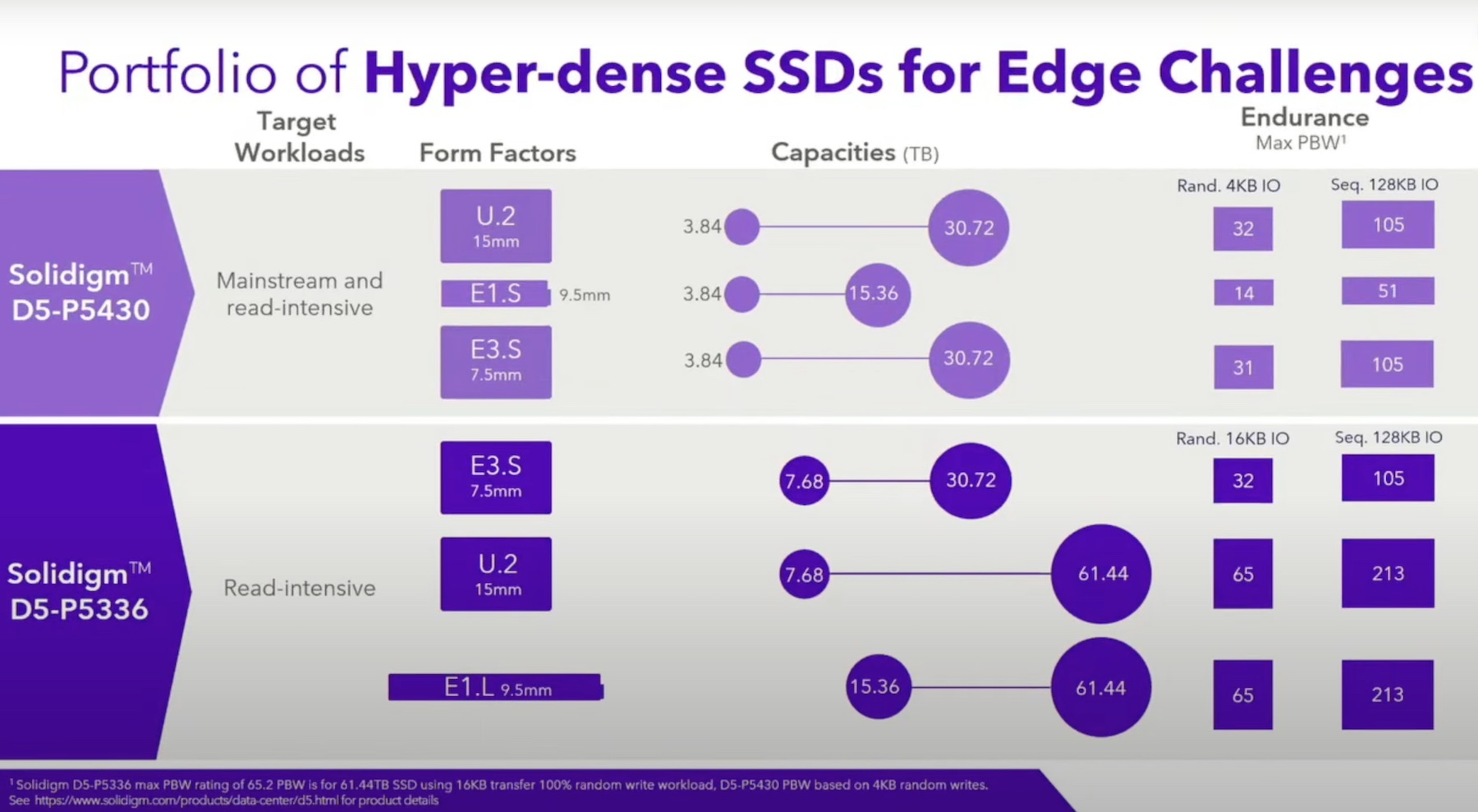
Another key advancement in SSD technology is the use of Quad-Level Cell (QLC) flash. QLC flash allows for higher storage capacities at a more affordable price point, making it an ideal choice for edge environments where cost-effectiveness and capacity are essential. Solidigm has proven the reliability of QLC flash over four generations of SSDs, and have demonstrated that this technology delivers the endurance and performance for use in edge servers.
Solidigm has recently introduced the next-generation D5-P5430 SSD lineup, including models specifically tailored to address the needs of edge environments. These SSDs are available in the new E3 form factor, which offers a perfect balance between efficiency and capacity in edge servers. The Solidigm D5-P5430 SSDs provide high performance, low power consumption, and strong endurance, ensuring smooth and reliable operations in demanding edge applications. With their compact size, these SSDs enable server vendors to maximize storage density, making them an excellent fit for edge deployments.

Stephen’s Stance: SSDs for the Edge
As the near edge becomes a focal point for delivering services and processing data, the value of advanced SSDs in edge environments cannot be overstated. These storage solutions offer the necessary performance, reliability, and efficiency required for the demanding nature of edge computing. Solidigm’s D5-P5430 SSDs, built on the proven reliability of QLC flash, provide a compelling solution for maximizing efficiency and capacity at the edge. Looking ahead, further advancements in SSD technology will continue to drive the capabilities and potential of edge environments, empowering organizations to unlock new possibilities and deliver unparalleled user experiences.
To learn more about Solidigm’s advanced SSDs, head to their website or watch our most recent Gestalt IT Roundtable with Solidigm and Supermicro.